|
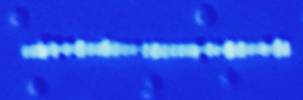
This image shows shape-selective aggregation of microdisks into columns using an entropic depletion attraction. The
aggregation is induced by adding additional sodium dodecyl sufate (SDS)
micelles. The osmotic pressure of these micelles causes disks to
aggregate face-to-face, whereas spheres (outside the column) do not
aggregate. The shape selectivity of the aggregation arises from very
different excluded volumes for the micelles for disks that nearly touch
as compared to spheres that nearly touch. This shape selectivity can be
used to purify disks from spheres in a mixed dispersion. See: "Osmotically Driven Shape Dependent Colloidal Separations", T.G. Mason, Phys. Rev. E Rapid Comm. 66, 060402 (2002).
|
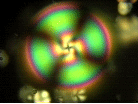
This image shows a microscopic liquid crystal droplet illuminated by white light using crossed polarizers. Studying the structure, interactions, and rheology of microscale and
nanoscale dispersions of particles such as these will lead to new
advances in the science of complex fluids.
|