|
 |
In simple distillation,
all of the material which is evaporated
and then condensed (the distillate) is collected together
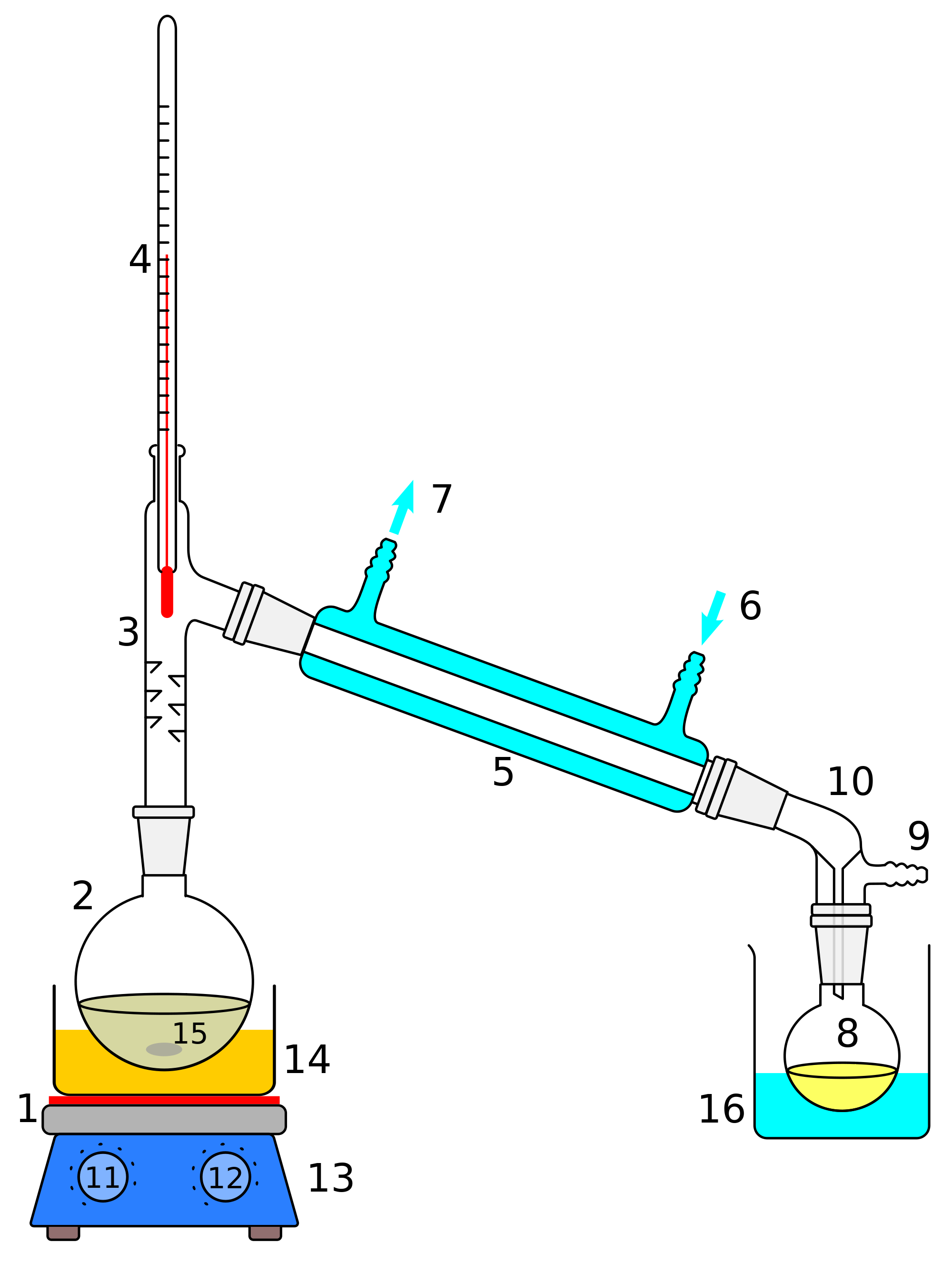
as a single fraction. Labeling code: (1) Heat source. (2)
Still pot. (3) Still head. (4) Thermometer. (5) Condenser.
(6) Cooling water
in. (7) Cooling water
out. (8) Distillate receiver. (9) Vacuum adapter. (10)
Still receiver. (11) Heat controller. (12) Stirrer
controller. (134) Stirrer/hot plate. (14) Heating bath.
(15) Stir bar. (16) Cooling bath. Click
here for a larger version. |
|
|
|
|

|
A still for making moonshine (illegal hard liquor) uses
simple distillation. The silver cylinder is the still pot
(which is heated by a wood fire), the copper tube is the
condenser, and the green barrel is the still pot.
Distillation of legal liquor is conducted in a distillery. |
|
|
|
|
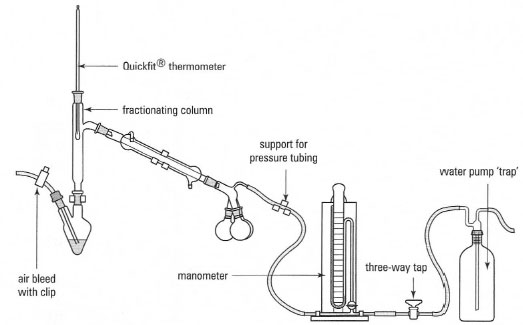 |
Fractional
distillation operates much like simple
distillation, except that the distillate is divided into
fractions. Each fraction might be a pure compound, or a
mixture with a different boiling
point range than other fractions. |
|
|
|
|
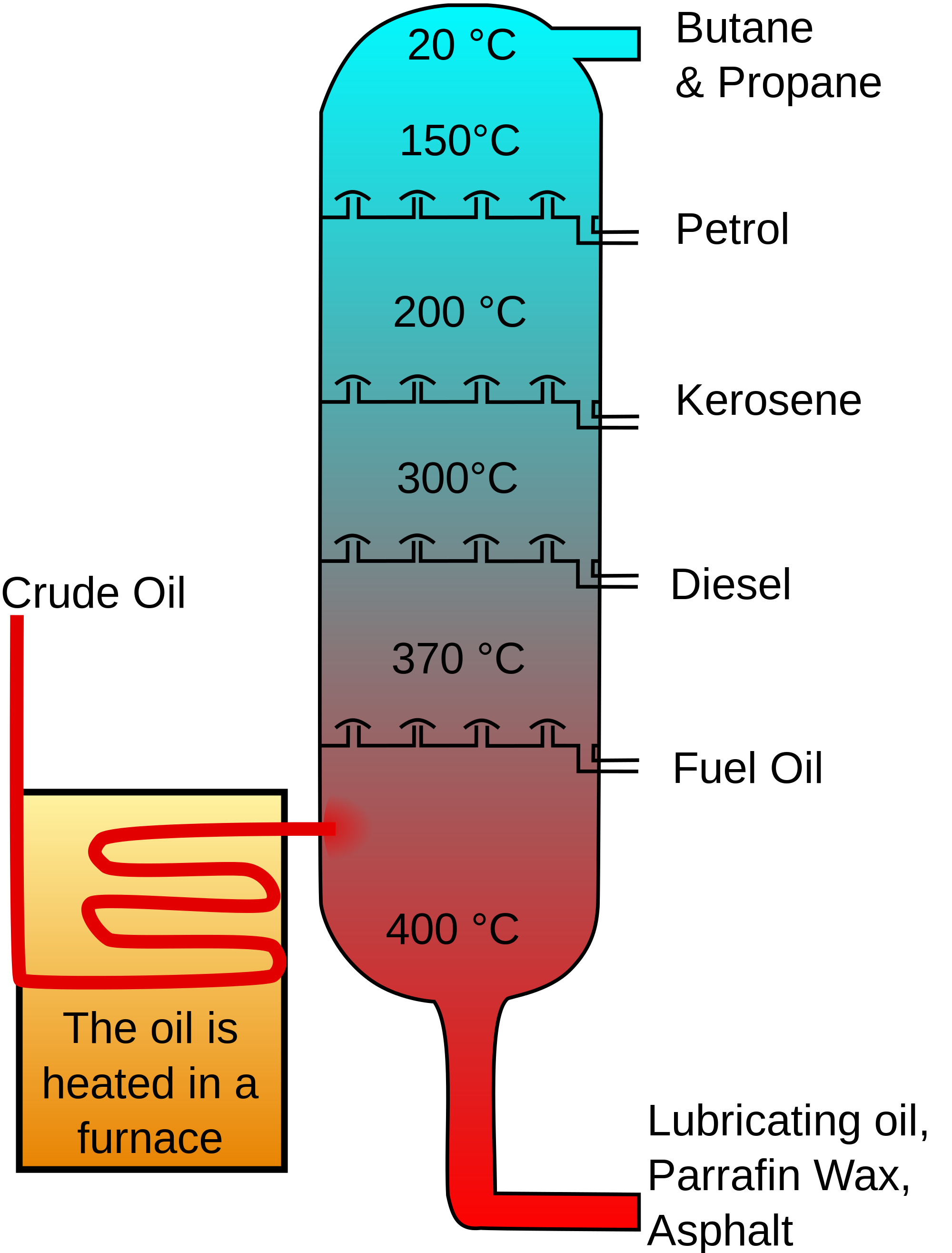 |
Diagram of a refinery's fractional
distillation column. An oil refinery uses fractional
distillation to separate crude
oil into material that have different boiling
point ranges. Gasoline,
composed mostly of C4 to C12 hydrocarbons,
is the fraction whose boiling
point range is about 40oC to about 200oC,
while
the kerosene/jet fuel fraction is composed mostly of C12
to C16 hydrocarbons
and has a boiling
point range is about 200oC to about 250oC. |
|
|
|
|

|
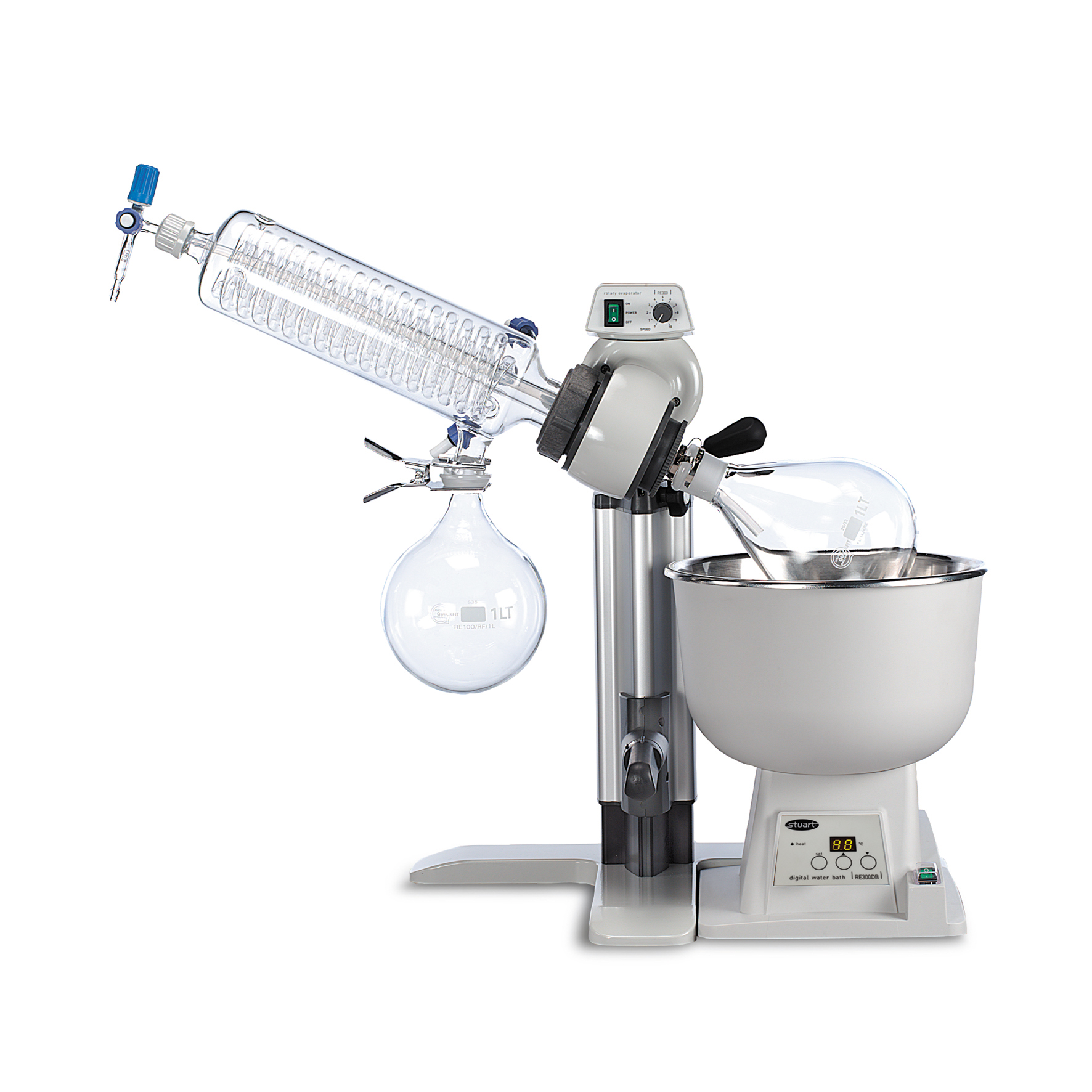
A rotary evaporator (rotovap) uses
simple vacuum
distillation to remove solvent
from a sample. As the ambient pressure is lowered, boiling
point is also lowered, so the solvent
evaporates more readily. |




