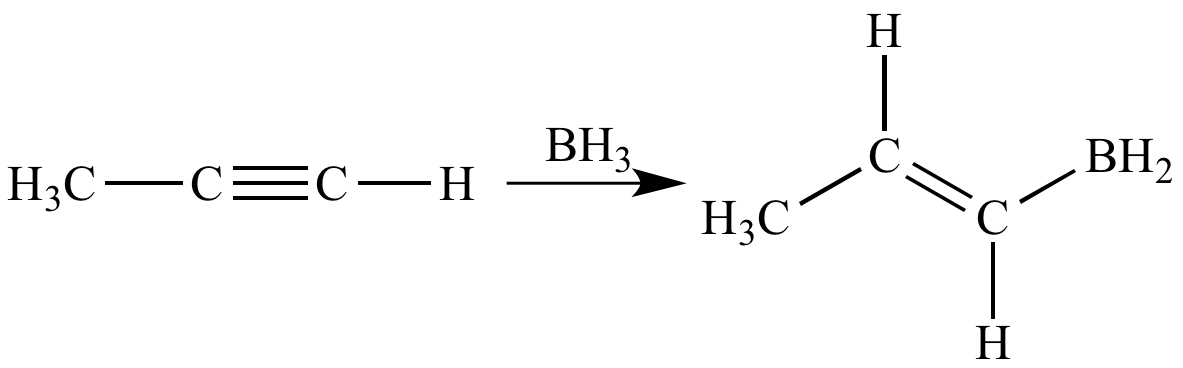
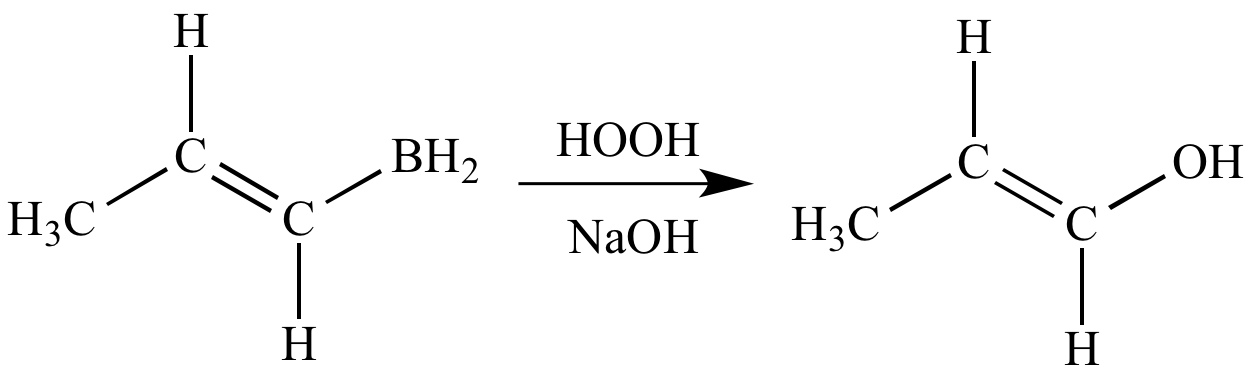
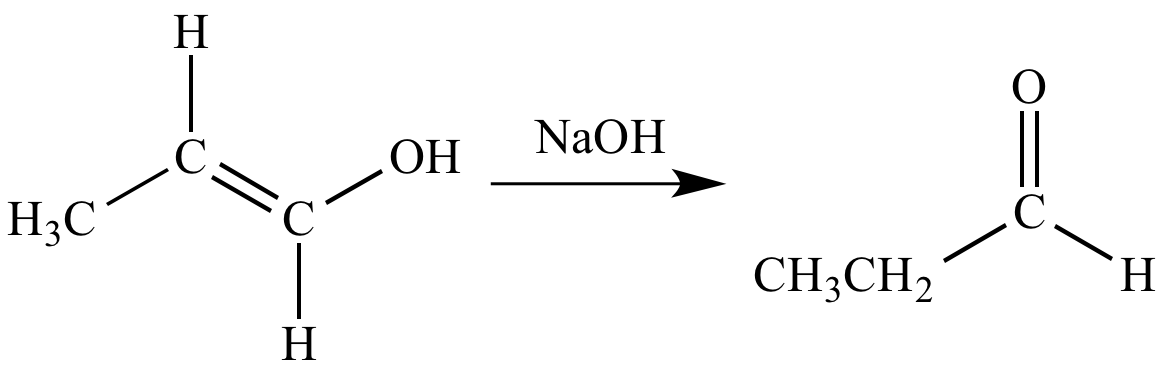
Hydroboration-oxidation
reaction:
A reaction in which an alkene
or alkyne
suffers hydroboration
to give an organoborane.
This organoborane
is then oxidized
to give an alcohol
(when the reactant
is an alkene),
a
ketone
(when the reactant
is an internal
alkyne), or an aldehyde
(when the reactant
is a terminal
alkyne). The net effect is the addition
of a molecule
of water
across the carbon-carbon pi
bond.
Steps in Hydroboration-Oxidation of an Alkene
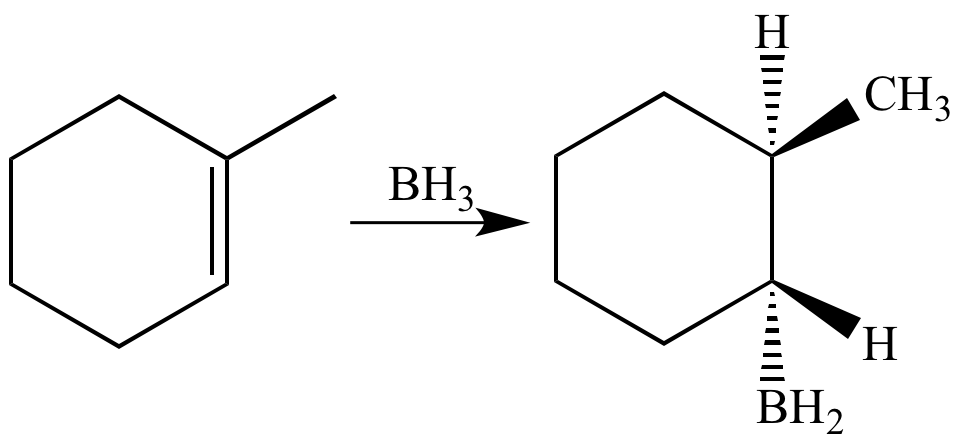
Borane (BH3) adds to methylcyclohexene in a syn manner to give an organoborane.
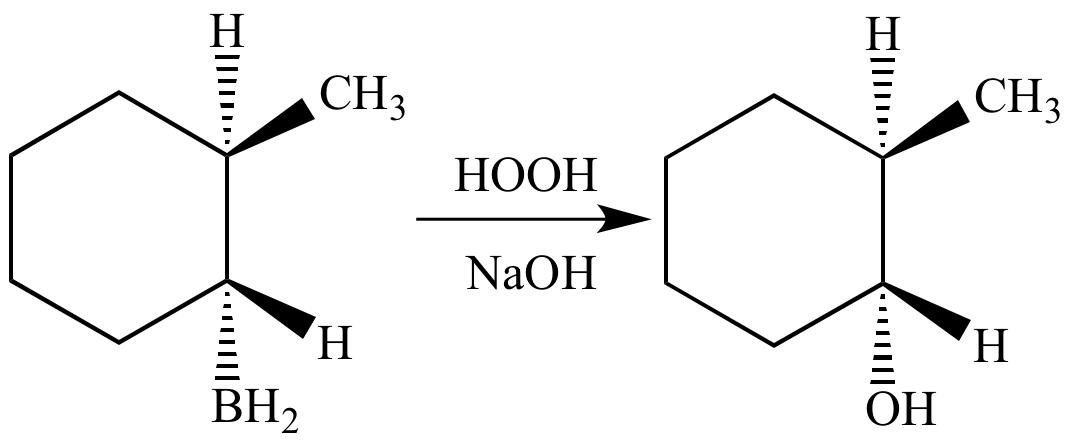
Oxidation of the organoborane with hydroxide ion (a strong base) and hydrogen peroxide converts the carbon-boron bond into an alcohol. Stereochemistry at the carbon atom that was bonded to the boron atom is retained. The net effect of the reaction is syn, anti-Markovnikov addition of water to the alkene pi bond.

Borane (BH3) adds to methylcyclohexene in a syn manner to give an organoborane.

Oxidation of the organoborane with hydroxide ion (a strong base) and hydrogen peroxide converts the carbon-boron bond into an alcohol. Stereochemistry at the carbon atom that was bonded to the boron atom is retained. The net effect of the reaction is syn, anti-Markovnikov addition of water to the alkene pi bond.