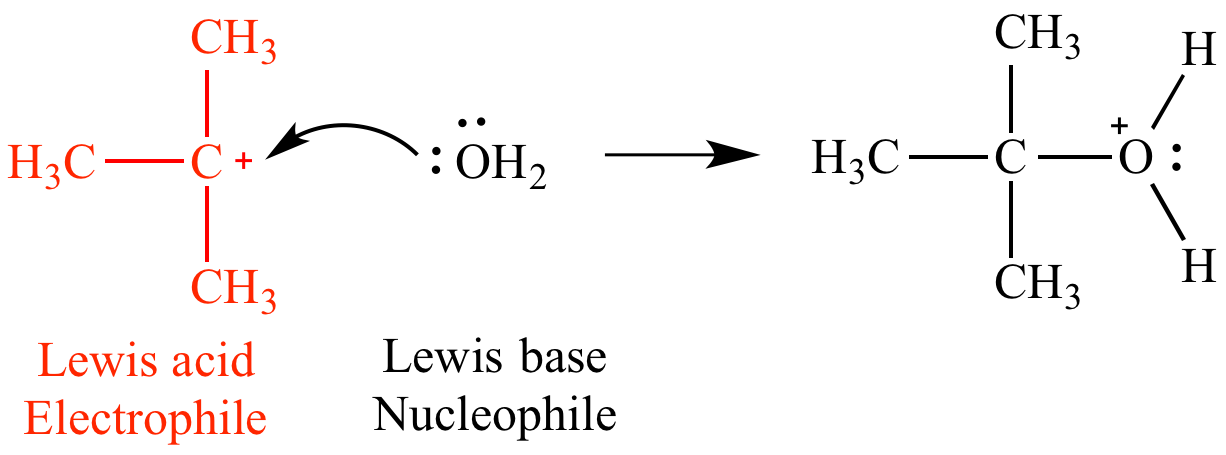
In this mechanism step the tert-butyl carbocation is a Lewis acid (an electrophile) because it is accepting an electron pair from water. This is an example of a Lewis acid which is not a Bronsted acid.
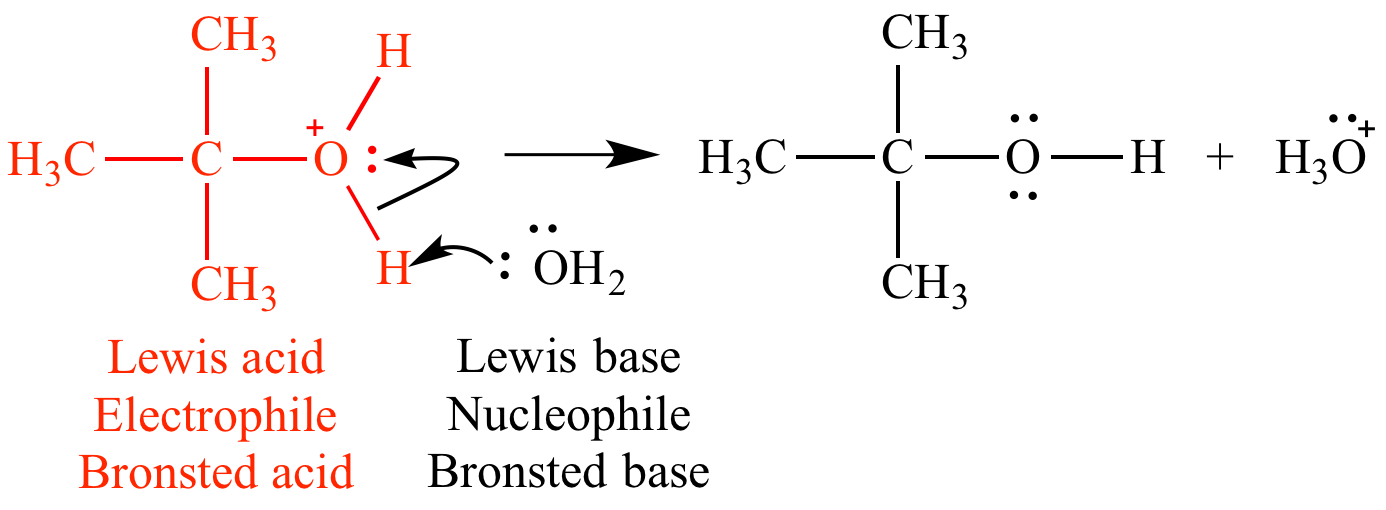
In this mechanism step the oxonium ion is a Lewis acid (an electrophile) because it is accepting an electron pair from water. The oxonium ion is also a Bronsted acid because it is donating a proton to water.